Erreur de format d'e-mail
emailCannotEmpty
emailDoesExist
pwdLetterLimtTip
inconsistentPwd
pwdLetterLimtTip
inconsistentPwd

Offer Technical Support and Customized Solutions
The company is committed to creating new and improved plastic materials to meet the evolving demands of the market.
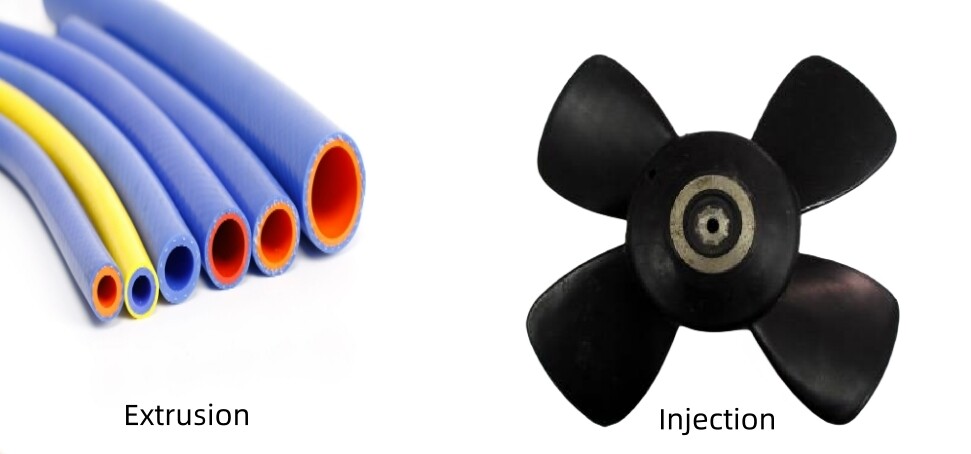
Injection Molding and Extrusion Molding: A Comprehensive Comparison
Introduction: In recent years, injection molding and extrusion molding techniques have emerged as the go-to manufacturing processes in various industries. These methods offer the ability to create intricate and complex designs with high precision, efficiency, and cost-effectiveness. This news article aims to provide a comprehensive overview of injection molding and extrusion molding, highlighting their key features, applications, and differences.
Injection Molding: Injection molding is a manufacturing process that involves injecting molten material into a mold cavity under high pressure. The molten material, usually a thermoplastic polymer, is injected into the mold through a nozzle. Once inside the mold, the material solidifies, creating a three-dimensional product. Injection molding is widely used for manufacturing precision components, such as small gears, medical equipment, and automotive parts. It offers a high level of repeatability, allowing manufacturers to produce identical products in large quantities.
Extrusion Molding: On the other hand, extrusion molding is a manufacturing process in which a continuously melted material, such as plastic, is forced through a die to create a uniform cross-sectional shape. The extruded material, typically in the form of rods, tubes, or sheets, is cooled and solidified to produce the final product. Extrusion molding finds its application in various industries, including construction, packaging, and automotive. It is particularly suitable for manufacturing items like plastic pipes, profiles, and film products.
Differences: While both injection molding and extrusion molding share similarities in terms of using melted material, they differ in several aspects. Firstly, injection molding is a closed mold system, whereas extrusion molding is an open mold system. Injection molding offers greater design flexibility, enabling intricate shapes and intricate details to be achieved with ease. In contrast, extrusion molding is better suited for creating uniform cross-sectional shapes with more straightforward designs.
Secondly, injection molding is primarily used for producing small to medium-sized finished products, while extrusion molding is more suitable for continuous production of longer sections, such as pipes or profiles.
Lastly, injection molding requires more complex machinery and higher initial investment due to the need for injection molding machines and molds. Extrusion molding, on the other hand, has comparatively simpler machinery and lower startup costs, making it a more accessible option for small businesses.
Conclusion: Injection molding and extrusion molding are two essential manufacturing processes that have revolutionized various industries. Each technique has its own unique advantages and applications, making them invaluable tools for creating a wide range of products. Understanding the differences between injection molding and extrusion molding allows manufacturers to choose the most suitable method for their specific requirements, resulting in efficient production and improved product quality.

